Sequenced Collections API - Sip of Java
Billy Korando on October 2, 2023
Annoyed by the boilerplate needed to find the last element in a collection, or to step through a collection in reverse order? The good news, those actions have become a lot easier to accomplish with the release of Java 21 and the Sequenced Collections API! Let’s take a look.
New Interfaces Same Hierarchy
The new Sequenced Collections API has been added as a series of new interfaces to the existing Collections Hierarchy for collections with a defined encounter order. In several cases the methods added to the new interfaces are actually existing methods that have been promoted from lower-level classes.
On the collections side, two new interfaces were added, SequencedCollection and SequencedSet:
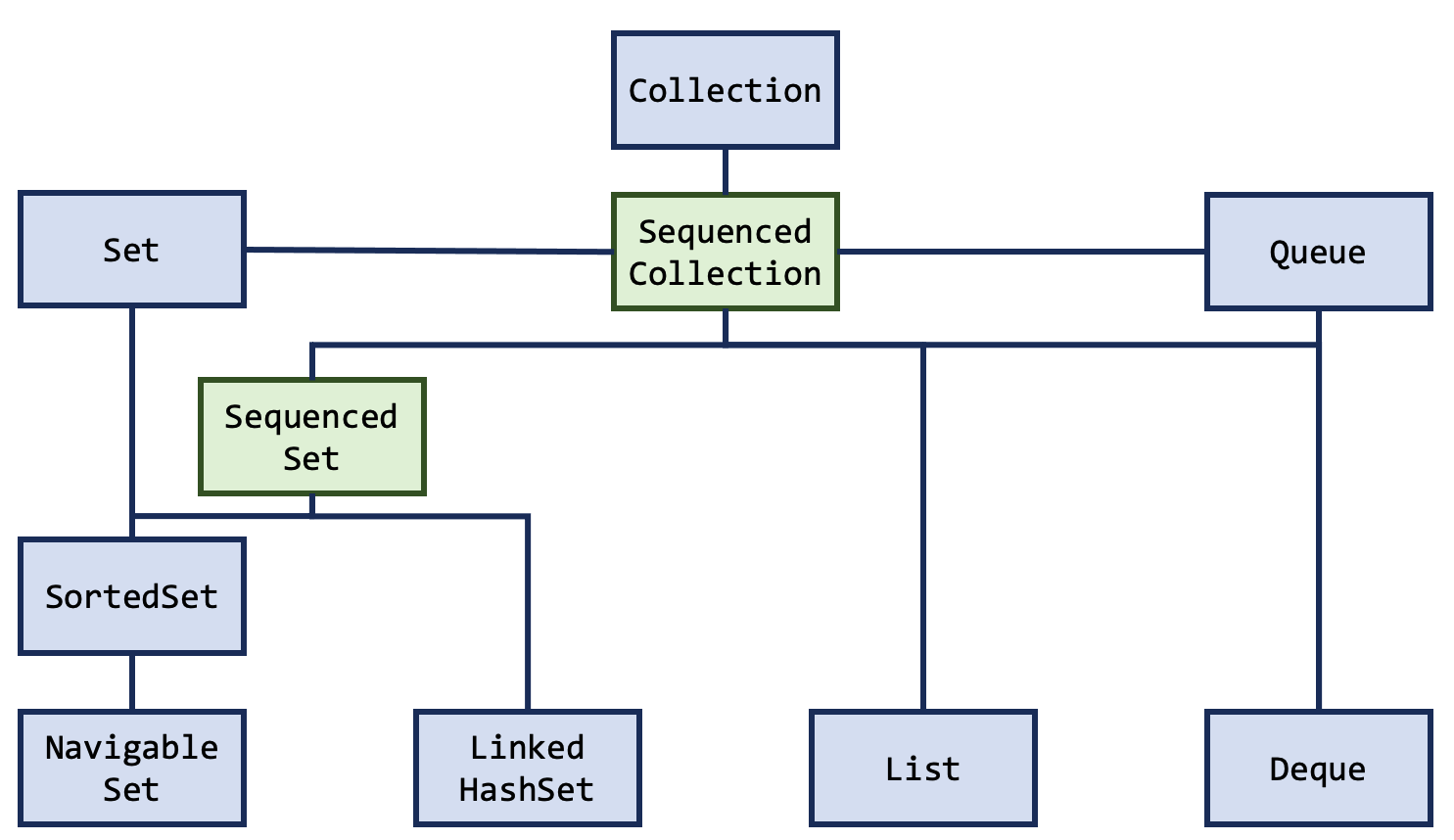
java.util.SequencedCollection contains the below methods:
interface SequencedCollection<E>
extends Collection<E> {
// New method
SequencedCollection<E> reversed();
// Methods promoted from Deque
void addFirst(E);
void addLast(E);
E getFirst();
E getLast();
E removeFirst();
E removeLast();
}
java.util.SequenceSet contains a single method, an override of reversed() which returns a SequencedSet instead:
interface SequencedSet<E> extends Set<E>,
SequencedCollection<E> {
// covariant override
SequencedSet<E> reversed();
}
On the Map side of the Collections Hierarchy a single interface was added SequencedMap:
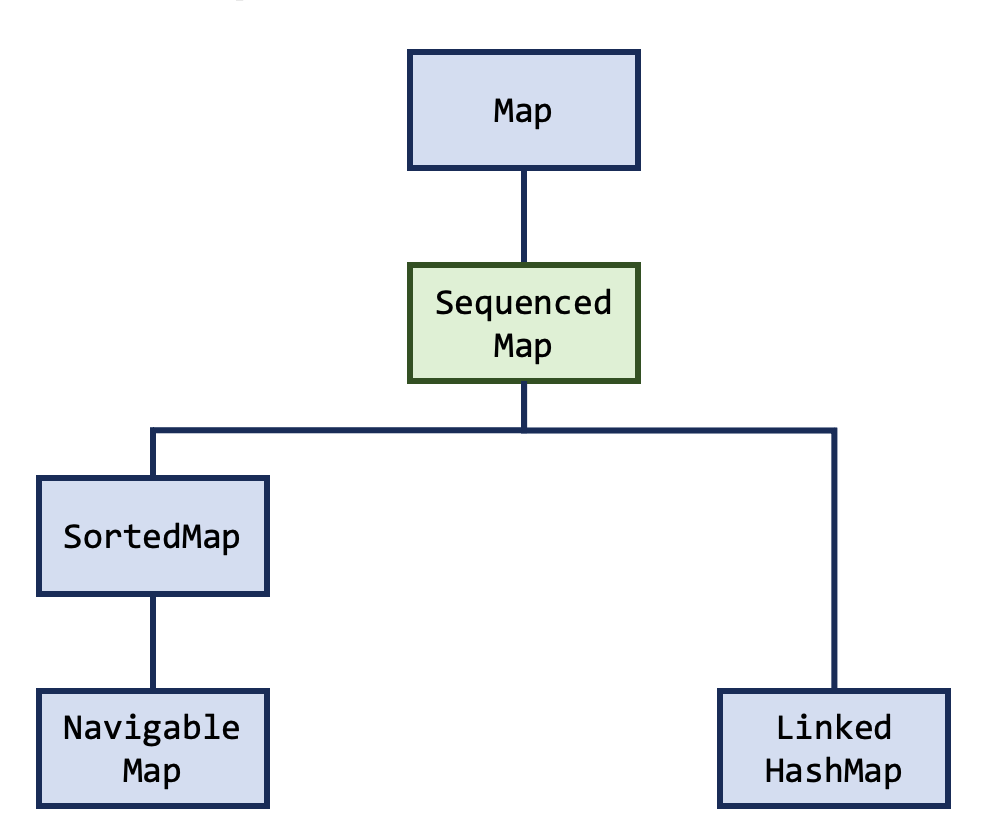
Here is a closer look at the contents of java.util.SequencedMap:
interface SequencedMap<K,V> extends Map<K,V> {
// new methods
SequencedMap<K,V> reversed();
SequencedSet<K> sequencedKeySet();
SequencedCollection<V> sequencedValues();
SequencedSet<Entry<K,V>> sequencedEntrySet();
V putFirst(K, V);
V putLast(K, V);
// methods promoted from NavigableMap
Entry<K, V> firstEntry();
Entry<K, V> lastEntry();
Entry<K, V> pollFirstEntry();
Entry<K, V> pollLastEntry();
}
Defined Encounter Order
As mentioned earlier the Sequenced Collections API updates collections with a defined encounter order. On the Collection tree this covers most of the popular and commonly used collections like ArrayList and SortedSet, though would exclude HashSet, which doesn’t have a defined encounter order.
For the Map tree the oft-used HashMap does not benefit from the Sequenced Collections API changes, as it does not have a defined encounter order. If you want to use the new methods defined in SequencedMap, you will need to use an alternative Map implementation like TreeMap, LinkedHashMap, or a Map implementing SortedMap.
Additional Reading
Sequenced Collections - JEP 431 Sequenced Collections - Inside Java Podcast 31
Happy coding!

